The Compound Effect in Programming & AI: How Small Improvements Lead to Big Results
Introduction: Small Steps, Big Results
Imagine improving your coding skills by just 1% every day. After a year, you'd be 37 times better than when you started. This is the compound effect—the principle that small, consistent actions accumulate into massive results over time.
In software development, artificial intelligence (AI), and IT education, this concept is transformative. Whether it's writing cleaner code, training smarter AI models, or mastering new technologies, incremental progress leads to exponential growth.
This article explores:
- The historical roots of iterative and incremental development.
- How the compound effect drives innovation in domain programming and AI.
- The challenges of incremental learning and adaptation.
- Practical strategies for continuous improvement in IT.
- The future of compound innovation in tech.
1. The Historical Context: From NASA to Agile
Iterative Development in Early Software Engineering
The idea of breaking work into small, repeatable cycles isn't new. In the 1960s, NASA's Project Mercury used iterative development to build reliable spacecraft software. Later, IBM applied the same approach in the Space Shuttle's avionics system, refining it over 17 iterations in 31 months.
The Rise of Agile and Lean
By the 2000s, Agile and Lean methodologies formalized these principles:
- Agile focuses on flexibility, collaboration, and continuous feedback.
- Lean eliminates waste by optimizing small, frequent improvements.
- Test-Driven Development (TDD) and Continuous Integration (CI) ensure quality through incremental testing.
These practices prove that small, consistent refinements lead to better software.
2. The Compound Effect in Domain Programming
Domain-Driven Design (DDD): Managing Complexity
Large software systems become unmanageable without structure. Domain-Driven Design (DDD) solves this by:
- Defining bounded contexts (clear problem boundaries).
- Using a ubiquitous language (shared terminology between developers and business experts).
- Breaking down complex domains into smaller, maintainable components.
Incremental Code Improvement
Instead of massive rewrites, successful teams apply:
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): Small, daily code refinements.
- Refactoring in Small Steps: Reducing technical debt without disrupting workflows.
- Feature Flags: Gradually rolling out changes to minimize risk.
"The best codebases evolve through compounding small improvements, not massive overhauls."
3. AI and the Power of Incremental Learning
How AI Learns Progressively
Unlike traditional models that train once, modern AI uses:
- Incremental Learning: Absorbing new data without forgetting old knowledge (e.g., recommendation systems).
- Transfer Learning: Applying learned patterns to new tasks (e.g., GPT models fine-tuning for specific uses).
- Compound AI Systems: Combining multiple AI models for complex reasoning (e.g., autonomous vehicles).
Challenges in AI's Compound Growth
- Bias Amplification: Small biases in training data can compound into major errors.
- Concept Drift: AI models must adapt as real-world data changes (e.g., stock market predictions).
- Validation Complexity: Ensuring reliability in multi-model AI systems is difficult.
4. Continuous Learning in IT: The Developer's Growth Mindset
The 1% Rule in Skill Development
Programming expertise isn't built overnight. Instead:
- Daily Micro-Learning: Spending 15–30 minutes daily on coding challenges compounds into mastery.
- Side Projects: Small experiments reinforce learning (e.g., building a personal API).
- Feedback Loops: Code reviews and pair programming accelerate improvement.
Avoiding "Tutorial Hell"
Many learners get stuck in an endless loop of tutorials. The solution?
✅ Build → Fail → Learn → Repeat ✅ Focus on one concept at a time (e.g., master arrays before diving into machine learning).
5. Challenges and How to Overcome Them
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Resistance to Change | Introduce small changes gradually (e.g., adopt one new tool per sprint). |
| Cognitive Overload | Break learning into micro-lessons (e.g., 20-minute daily coding sessions). |
| Bias in AI Models | Regularly audit training data and fine-tune models. |
| Legacy Code Refactoring | Refactor in small, testable increments. |
6. The Future: Compound Innovation in Tech
AI as a Catalyst for Change
- Automating Repetitive Tasks: Freeing developers to focus on innovation.
- Self-Improving Systems: AI that learns and adapts in real-time (e.g., DevOps automation).
Sustainable Software Development
- Green Coding: Small optimizations that reduce energy consumption.
- Modular Architectures: Easier to update and maintain over time.
The Next Wave: AI-Augmented Development
Tools like GitHub Copilot already show how AI can compound developer productivity by suggesting code snippets, fixing bugs, and automating boilerplate.
Conclusion: Start Small, Think Big
The compound effect isn't just a theory—it's a proven strategy in software engineering, AI, and skill development. By focusing on small, consistent improvements, you can:
✔ Write cleaner, more maintainable code. ✔ Build AI systems that learn and adapt. ✔ Master new technologies faster.
Your Action Plan:
- Commit to 1% daily improvement (e.g., one new Git command per day).
- Apply incremental refactoring (e.g., improve one function each week).
- Experiment with compound AI tools (e.g., AutoML for model tuning).
"Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated daily." — Robert Collier
Further Reading
- Books: Atomic Habits (James Clear), The Pragmatic Programmer (Andrew Hunt)
This article explores the transformative power of incremental improvement in technology. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting your coding journey, understanding the compound effect can accelerate your growth and success in the ever-evolving world of programming and AI.
Master AI Development
Get hands-on with our comprehensive AI tutorials and projects
Explore AI ProjectsTags
Related Articles

How to Protect Your Data in the Age of AI
Discover six essential strategies to protect your data in the era of Artificial Intelligence. Learn about modern threats, governance, encryption, and real-world case studies to secure your business and gain a competitive edge.
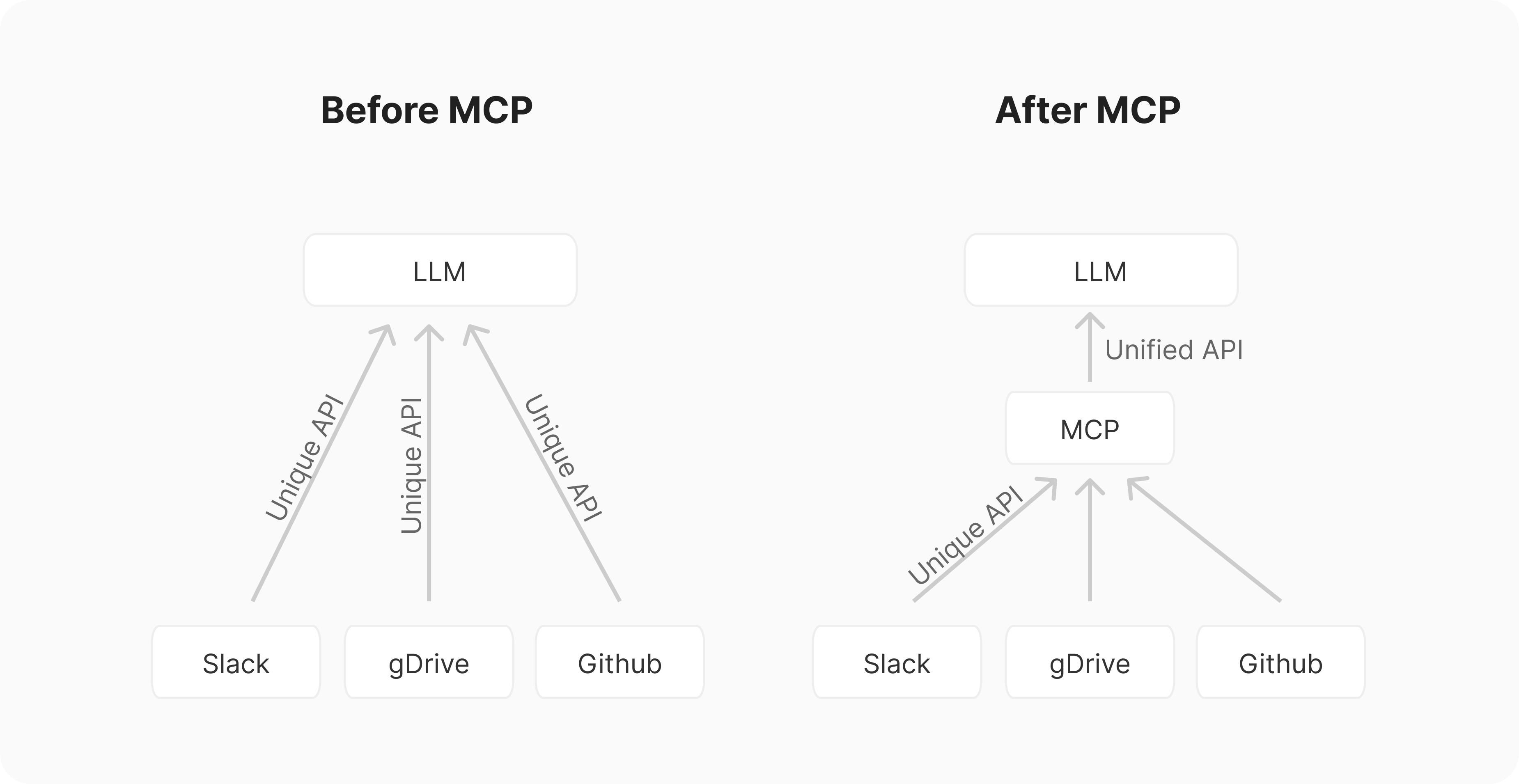
The Model Context Protocol: The New Standard for AI Integration
Explore the Model Context Protocol (MCP), the revolutionary open standard that's transforming how AI systems connect with external data sources and tools. Learn how MCP is solving the M×N integration problem and enabling seamless AI applications.

Python Playground: A Fun, Project-Based Guide to Learning Python for Generative AI
Learn Python through hands-on projects! This beginner-friendly guide walks you through building an AI-powered text adventure game while mastering Python fundamentals in a fun and engaging way.

The Complete Guide to OpenAI API: A Practical Developer's Handbook
Explore a complete guide to the OpenAI API, covering everything from setup and core functionality to advanced features, performance optimization, error handling, and practical use cases. Perfect for developers looking to integrate and leverage OpenAI models effectively.
About the Author

Hafida Belayd
A passionate Data Analyst and technologist exploring the intersections of data and creativity.